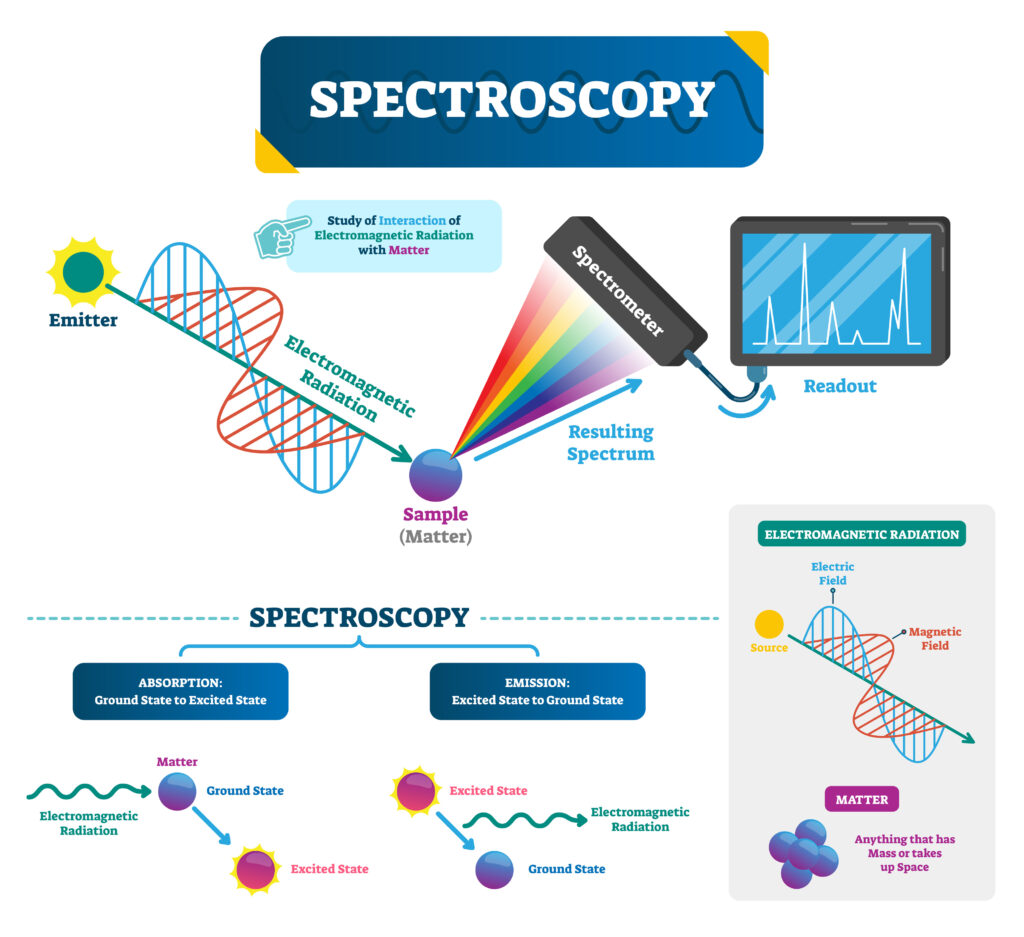
Raman spectrophotometry enables quick and precise evaluation of a sample's chemical composition and molecular structure and is a beneficial analytical tool in drug quality control.
Detecting active ingredients and contaminants in medicine samples is one of the most essential uses of Raman spectrophotometry in medication quality control. Raman spectroscopy makes it possible to identify the substance in the sample by determining the distinctive spectral lines of a substance. Also, this method can find contaminants that might compromise the drug's effectiveness or safety.